The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
Understanding the Differences: Are Eczema and Psoriasis the Same?
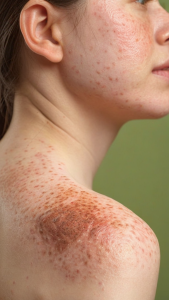
When you notice red, itchy patches on your skin, it can be hard to understand what’s happening. If you’ve heard of eczema and psoriasis, you might wonder: are eczema and psoriasis the same? Both are common skin conditions, but they have distinct differences that are important to recognize for effective treatment.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, primarily affects children but can continue into adulthood. It causes dry, itchy skin that can become inflamed. On the other hand, psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that speeds up the life cycle of skin cells, leading to thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. While both conditions can cause discomfort, their causes, symptoms, and treatments differ significantly.
Key Differences Between Eczema and Psoriasis
- Causes: Eczema is often triggered by environmental factors, allergens, or stress, while psoriasis is an autoimmune response where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
- Symptoms: Eczema typically presents as dry, cracked skin with intense itching. Psoriasis, however, has a more pronounced appearance with thick, scaly patches.
- Location: Eczema commonly appears on the insides of elbows and knees, while psoriasis often affects the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
- Age of Onset: Eczema usually starts in childhood, while psoriasis can develop at any age, though it often appears in young adulthood.
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
Understanding the symptoms of each condition can help you identify what you might be dealing with. Eczema tends to make the skin red and oily or scaly, and in kids, it may also generate small, raised bumps that can leak a clear fluid if scratched. With psoriasis, affected areas are usually very dry and thick, with a silvery scale. It’s crucial to observe your symptoms closely and consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosis for Eczema and Psoriasis
Diagnosing eczema involves a physical examination, focusing on the skin’s appearance and location. A doctor might also ask about your family history and any recent allergies. In contrast, diagnosing psoriasis may also include a skin biopsy to distinguish it from other skin disorders.
Living with Eczema and Psoriasis
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
Both eczema and psoriasis can impact daily activities. The itching and discomfort associated with these conditions can disrupt sleep, lead to anxiety, and affect social interactions. Managing these conditions often requires a holistic approach that involves skincare routines, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Treatment Options
The treatments for eczema and psoriasis can overlap, but they typically focus on different aspects of each condition:
- Eczema Treatments: Over-the-counter creams and ointments, topical corticosteroids, and antihistamines to reduce itching are common. Moisturizing regularly can help prevent flare-ups.
- Psoriasis Treatments: Treatments may include topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications that can help control the immune response.
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
Finding the right treatment often requires a bit of trial and error. Work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a management plan tailored to your needs. Remember, what works for one person may not work for another.
Preventing Flare-Ups
To minimize flare-ups of either condition, consider these prevention strategies:
- Maintain skin hydration by using fragrance-free moisturizers.
- Avoid known irritants such as harsh soaps or certain fabrics.
- Manage stress through mindfulness or relaxation techniques.
- Monitor your diet for potential allergens.
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
While eczema and psoriasis share some similarities, they are fundamentally different in their causes and treatments. Understanding these differences is essential for managing symptoms effectively. If you’re experiencing skin issues, seek the guidance of a healthcare professional who can help you navigate the path to healthier skin.
Common Treatments for Eczema and Psoriasis: What Works Best?
Eczema and psoriasis are two common skin conditions that often cause confusion due to their similar appearances and overlapping symptoms. However, understanding their distinct characteristics and effective treatments is essential for managing these conditions effectively. Let’s explore the most common treatments available for both eczema and psoriasis, and discuss what might work best for you.
Understanding Eczema and Psoriasis
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic condition characterized by itchy, inflamed skin. It can appear anywhere on the body, but it’s most commonly found in the flexural areas, such as the insides of the elbows or behind the knees. On the other hand, psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that leads to the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in thick, red, scaly patches on the skin, often seen on the elbows, knees, and scalp. While both conditions are chronic and can flare up, they require different treatment approaches.
Topical Treatments
The first line of treatment for both eczema and psoriasis often involves topical medications. These can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
- Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments are commonly prescribed for both conditions. They help reduce itching and redness. However, they should be used with caution, especially for eczema, as long-term use can lead to skin thinning.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: These creams, like tacrolimus or pimecrolimus, are often used to treat eczema, showing effectiveness in reducing flare-ups without the side effects associated with corticosteroids. They work by suppressing the immune response in the skin.
- Vitamin D Analogues: These are especially useful for treating psoriasis. Calcipotriene and calcitriol are popular choices that help control skin cell production, easing the symptoms of psoriasis.
- Retinoids: Topical retinoids, such as tazarotene, can help slow down the skin cell growth associated with psoriasis, making them beneficial for certain cases.
Systemic Treatments
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
When topical treatments are not sufficient, systemic treatments may be needed for both conditions. These treatments are taken orally or by injection and work throughout the body.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine and methotrexate can be used for severe psoriasis. They suppress the immune system, helping to decrease skin cell production and alleviate symptoms.
- Biologics: For moderate to severe psoriasis, biologic drugs like adalimumab and etanercept target specific parts of the immune system. They are particularly effective for psoriasis and have shown promise for some cases of eczema as well.
Phototherapy
Another option for both eczema and psoriasis is phototherapy, which involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light. This treatment can help reduce symptoms and flare-ups. It is particularly useful for psoriasis, as it slows the growth of skin cells. For eczema, phototherapy can help improve skin hydration and reduce inflammation. However, it usually requires multiple sessions and supervision by a healthcare professional.
Natural Remedies
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
Some people find relief from mild eczema or psoriasis symptoms using natural remedies. Always consult your doctor before trying these options to ensure they don’t interfere with existing treatments.
- Moisturizers: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential for both conditions. Use fragrance-free, thick creams or ointments regularly to maintain skin moisture.
- Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal baths can help soothe irritated skin and reduce itching for eczema sufferers.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Some people report that diluted apple cider vinegar can help alleviate itching associated with eczema.
Finding the right treatment for eczema and psoriasis may take time and experimentation, as everyone’s skin reacts differently. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan that fits your unique needs. By understanding the options available and what works best for your condition, you can manage symptoms more effectively and improve your quality of life.
Conclusion
Recognizing the distinctions between eczema and psoriasis is crucial for managing these skin conditions effectively. Both ailments may exhibit some similar symptoms, such as redness and itchiness, but they stem from different causes and require unique treatment approaches. Psoriasis primarily results from an immune response that accelerates skin cell turnover, while eczema often relates to environmental factors, allergies, or stress.
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
When considering treatments, it’s important to use strategies specific to each condition. For eczema, moisturizers, topical steroids, and antihistamines can offer relief by hydrating the skin and reducing inflammation. On the other hand, psoriasis may benefit from therapies that target immune responses, such as topical treatments, phototherapy, or systemic medications.
Understanding what works best for your skin condition empowers you to seek the right solutions. If you suspect you have either eczema or psoriasis, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. They can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific needs and condition severity.
The Brain Song reactivates this hidden power using soundwave technology. Just listen 7 minutes a day and feel the difference.
By identifying whether you are dealing with eczema or psoriasis, you can make informed choices about your treatment plan. Every person’s skin is unique, and finding the right approach may take some time. With the proper understanding and care, you can effectively manage these conditions and enhance your overall skin health.